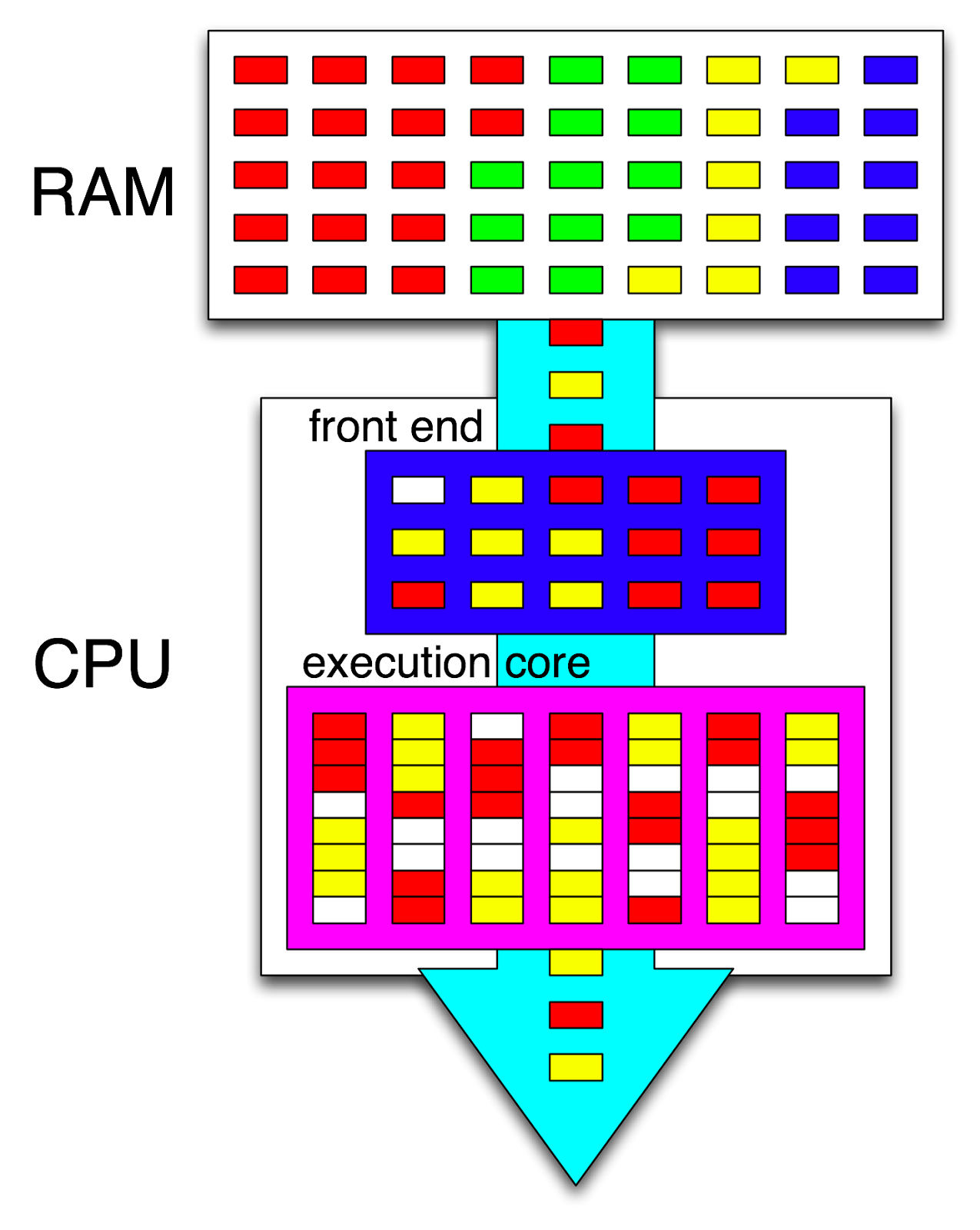
Hyper-Threading is
a technology used by some Intel microprocessor s that allows a single microprocessor
to act like two separate processors to the operating system and the application
program s that use it. It is a feature of Intel's IA-32 processor architecture.
With Hyper-Threading, a
microprocessor's "core" processor can execute two (rather than one)
concurrent streams (or thread s) of instructions sent by the operating system.
Having two streams of execution units to work on allows more work to be done by
the processor during each clock cycle . To the operating system, the
Hyper-Threading microprocessor appears to be two separate processors. Because
most of today's operating systems (such as Windows and Linux) are capable of
dividing their work load among multiple processors (this is called symmetric
multiprocessing or SMP ), the operating system simply acts as though
the Hyper-Threading processor is a pool of two processors
No comments:
Post a Comment